 |
| Java 8 Stream Api Collect Method |
What is collect() method in Java 8?
Collect() method of java8 stream api is terminal method. It performs a mutable reduction operation on the element of the stream.
A mutable reduction operation process the stream elements and then accumulate it into a mutable result container. Once the elements are processed, a combining function merges all the result containers to create the result.
Learn Difference between Intermediate and Terminal Operations :-
There is two variant of collect method.
- collect(Supplier supplier, BiConsumer accumulator, BiConsumer combiner)
- collect(Collector collector)
- supplier: It is a function that creates a new mutable result container. For the parallel execution, this function may be called multiple times and it must return a fresh value each time.
- accumulator: it is a stateless function that must fold an element into a result container.
- combiner: It is a stateless function that accepts two partial result containers and merges them, which must be compatible with the accumulator function.
Lets see example of 1st collect method.
Example 1 :- Concat list of string using stream and parallel stream
public class CollectMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> vowels = List.of("a", "e", "i", "o", "u");
// sequential stream - nothing to combine
StringBuilder result = vowels.stream()
.collect(StringBuilder::new, (x, y) -> x.append(y),
(a, b) -> a.append(",").append(b));
System.out.println(result.toString());
// parallel stream - combiner is combining partial results
StringBuilder result1 = vowels.parallelStream()
.collect(StringBuilder::new, (x, y) -> x.append(y),
(a, b) -> a.append(",").append(b));
System.out.println(result1.toString());
}
}
Output :-
aeiou
a,e,i,o,u
- The supplier function is returning a new StringBuilder object in every call.
- The accumulator function is appending the list string element to the StringBuilder instance.
- The combiner function is merging the StringBuilder instances. The instances are merged with each other with a comma between them.
- In the first case, we have a sequential stream of elements. So they are processed one by one and there is only one instance of StringBuilder. There is no use of the combiner function. That’s why the output produced is “aeiou”.
- In the second case, we have a parallel stream of strings. So, the elements are processed parallelly and there are multiple instances of StringBuilder that are being merged by the combiner function. Hence, the output produced is “a,e,i,o,u”.
Now lets see second collect method.
collect(Collector collector)
Example 2 :- Collectors.toList()
Collectors.toList() method is used to convert stream into list.
Example 3 :- Collectors.toSet()
Collectors.toSet() method is used to convert into set.Example 4 :- Collectors.toMap()
Collectors.toMap() method is used to convert stream into map.
In map we have key and value, and in list we have single values so we use list values as key and values length as values.
Example 5 :- Collectors.toCollection
As you probably already noticed, when using toSet and toList collectors, you can't make any assumptions of their implementations. If you want to use a custom implementation, you will need to use the toCollection collector with a provided collection of your choice.
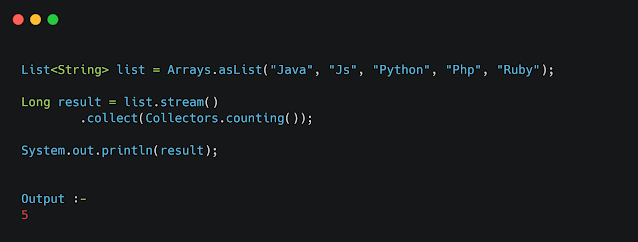
Example 6 :- Collectors.counting()
Return number of value in given stream.
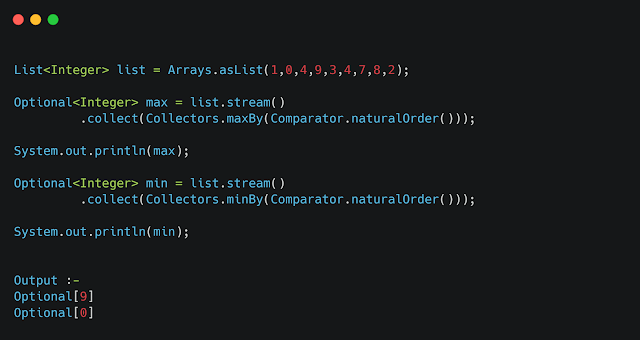
Example 7 :- Collectors.maxBy() / minBy()
MaxBy/MinBy collectors return the biggest/the smallest element of a Stream according to a provided Comparator instance.
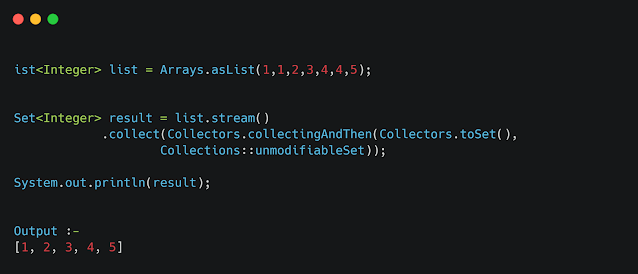
Example 8 :- Collectors.collectingAndThen()
CollectingAndThen is a special collector that allows performing another action on a result straight after collecting ends.
Let's collect stream elements to a set instance and then convert the result into an immutableSet instance:
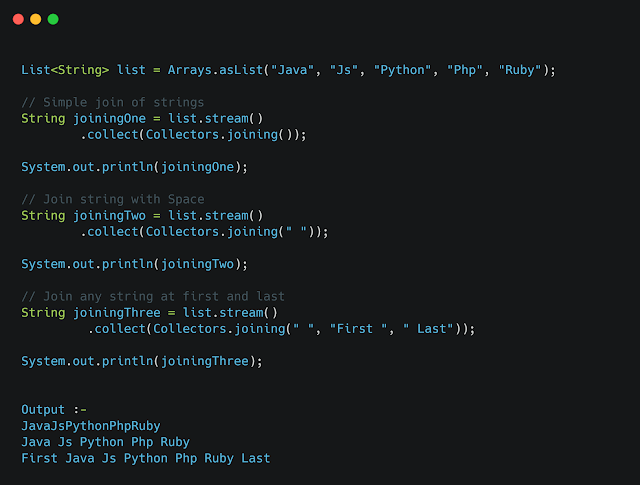
Example 9 :- Collectors.joining()
- Returns a
Collectorthat concatenates the input elements into aString, in encounter order. - Returns a
Collectorthat concatenates the input elements, separated by the specified delimiter, in encounter order. - Returns a
Collectorthat concatenates the input elements, separated by the specified delimiter, with the specified prefix and suffix, in encounter order.
There are also others methods available you can check out that in java doc.
Other Java 8 Methods :-




Comments
Post a Comment