Spring Boot application with Thymeleaf, Rest API, JPA and MySql Database
In this article, we will seen how to create simple Spring boot application with Create, Read, Update and Delete operations with MySql and Thymeleaf.
But first checkout what is Thymeleaf?
Thymeleaf :-
Thymeleaf is modern server side Java template engine for web and standalone environment. Thymeleaf's main goal is to bring elegant natural templates to your development workflow — HTML that can be correctly displayed in browsers and also work as static prototypes, allowing for stronger collaboration in development teams.
So lets start our Tutorial :-
First learn how to create Spring Boot application with Rest API, JPA and Mysql.
Project Structure :-
For Create Spring Boot project and Sql table click on Above given link.
1. Configure Maven Dependency
For work with Thymeleaf we have to include "spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf" Dependency.
We are also adding "mysql-connector-java" dependency for connecting web application with MySql database.
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.1</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootCrudWithThymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SpringBootCrudWithThymeleaf</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.34</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2. Add application.properties file
In application.properties file, we will define Mysql database connection properties.
- datasource url
- datasource driverClassName
- datasource username
- datasource password
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = root
#The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
3. Create Model Class
package com.example.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "book")
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int id;
@Column
private String bookname;
@Column
private String author;
@Column
private int price;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getBookname() {
return bookname;
}
public void setBookname(String bookname) {
this.bookname = bookname;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
3. Create Repository Interface
package com.example.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.example.model.Book;
public interface BookRepository extends JpaRepository<Book, Integer> {
}
4. Create Service class
package com.example.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.model.Book;
import com.example.repository.BookRepository;
@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
BookRepository bookRepository;
public List<Book> loadAllBooks() {
return (List<Book>) bookRepository.findAll();
}
public Book loadBookById(int id) {
return bookRepository.findById(id).get();
}
public Book saveBook(Book book) {
bookRepository.save(book);
return loadBookById(book.getId());
}
public void deleteBook(int id) {
bookRepository.deleteById(id);
}
public Book updateBook(Book book) {
return bookRepository.save(book);
}
}
5. Create Controller class
package com.example.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import com.example.model.Book;
import com.example.service.BookService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
BookService bookService;
@RequestMapping( method = RequestMethod.GET)
private String getAllBooks(Model model) {
List<Book> list = bookService.loadAllBooks();
model.addAttribute("allBooks", list);
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/new")
public String showNewBookPage(Model model) {
Book book = new Book();
model.addAttribute("book", book);
return "add-book";
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/save", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String saveNewBook(@ModelAttribute("book") Book book) {
bookService.saveBook(book);
return "redirect:/books";
}
@GetMapping("/edit/{id}")
private String editBook(@PathVariable("id") int id, Model model) {
Book book = bookService.loadBookById(id);
model.addAttribute("book", book);
return "edit-book";
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/update/{id}", method = RequestMethod.POST)
private String updateBook(@PathVariable("id") int id, @ModelAttribute Book book) {
book.setId(id);
bookService.updateBook(book);
return "redirect:/books";
}
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
private String deleteBook(@PathVariable("id") int id) {
bookService.deleteBook(id);
return "redirect:/books";
}
}
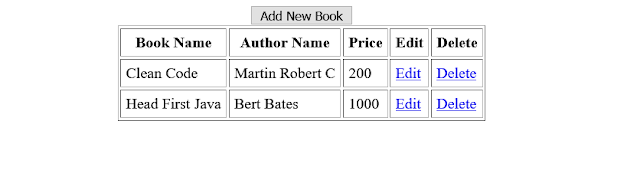
Now we create index file that displays all books that are stored on our database. You can see in "getAllBooks()" method we returns a "index" as string means index.html page.
For run the project right click on project and click on Run As -> Spring Boot App
Enter http://localhost:8080/books in browser
Display or Read
index.html
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<body>
<div align="center">
<a href="/books/new">
<button>Add New Book</button>
</a>
<table border="1" cellpadding="5">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Book Name</th>
<th>Author Name</th>
<th>Price</th>
<th>Edit</th>
<th>Delete</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="book : ${allBooks}">
<td th:text="${book.bookname}"></td>
<td th:text="${book.author}"></td>
<td th:text="${book.price}"></td>
<td>
<a th:href="@{/books/edit/{id}(id=${book.id})}">Edit</a>
</td>
<td>
<a th:href="@{/books/delete/{id}(id=${book.id})}">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</body>
</html>
So lets see how its looks like
Create or Add
add-book.html
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Add New Book</title>
</head>
<body>
<div align="center">
<form action="#" th:action="@{/books/save}" th:object="${book}" method="post">
<table border="0" cellpadding="10">
<tr>
<td>Book Name:</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{bookname}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Author:</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{author}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Price:</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{price}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2"><button type="submit">Save</button> </td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Update
edit-book.html
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Update Book</title>
</head>
<body>
<div align="center">
<form action="#" th:action="@{/books/update/{id}(id=${book.id})}" th:object="${book}" method="post">
<table border="0" cellpadding="10">
<tr>
<td>Book Name:</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{bookname}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Author:</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{author}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Price:</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{price}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2"><button type="submit">Save</button> </td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
In edit operation we update the "Head First Java" book price 1000 to 2000
Delete :-
For delete operation simply click on delete link and its done.
If you have any query regrading above tutorial comment down.
See Related Article :-
- Spring Boot Crud operation with Rest Api + MySql + Jpa
- Difference between CrudRepository and JpaRepository
- Role based Authorization (Admin and Other User) and Permissions in Spring Security with Spring Boot





Thanks for sharing this article. However, I am asking you to please add user roles authorization.
ReplyDeleteThank you for reading and suggestion.
DeleteI have added Authentication and Authorization using Spring Security, you can check out here.
https://uniquethrowdown.blogspot.com/2021/11/authentication-and-authorization-in-spring-security.html